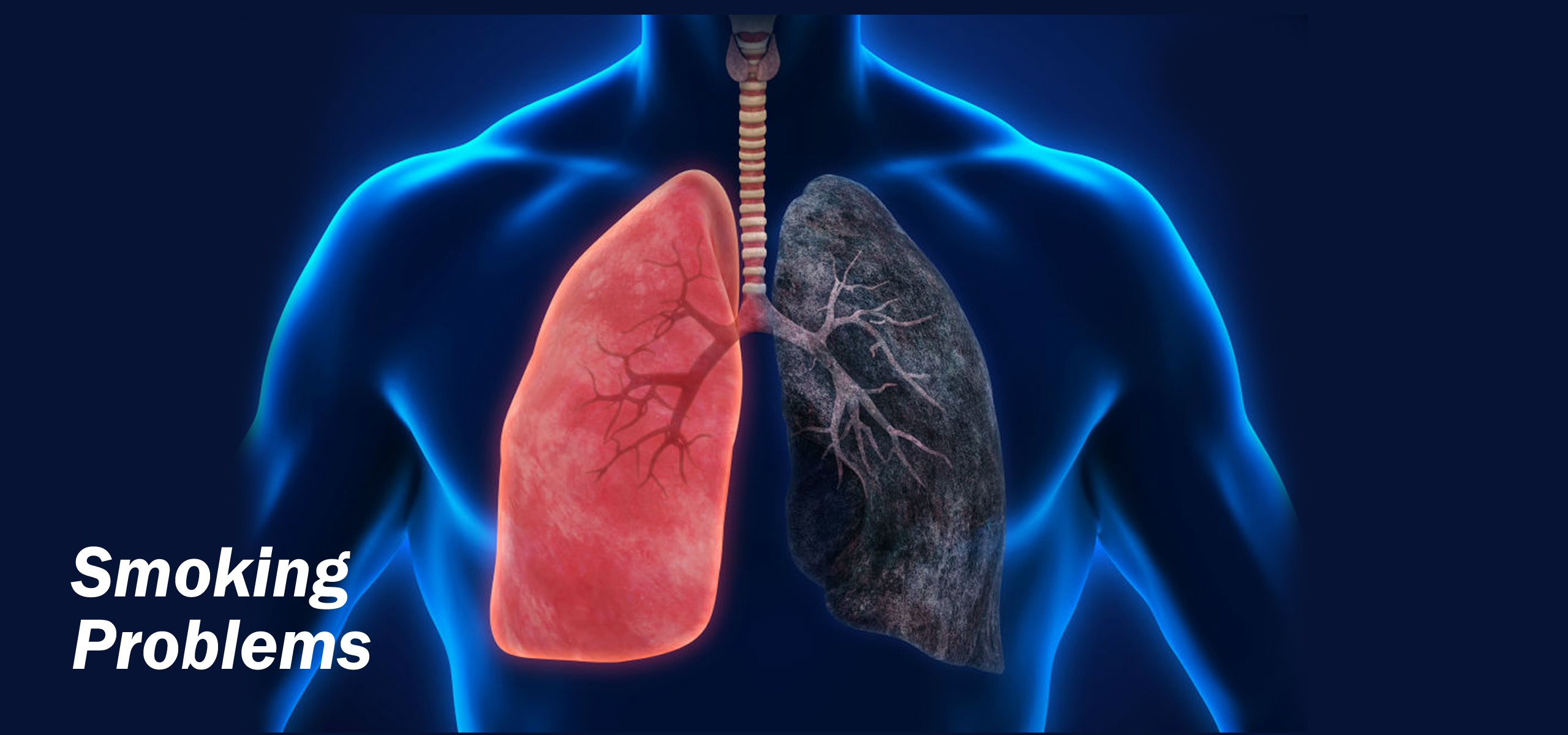
Smoking causes cancer, heart disease, stroke, lung diseases, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Smoking also increases risk for tuberculosis, certain eye diseases, and problems of the immune system, including rheumatoid arthritis.
Smoking Related Diseases
-
Bad breath and yellowing of the teeth.
-
Cold hands and feet.
-
Frequent or recurrent lung infections
-
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
-
Loss of taste and smell.
After 5–15 years: The risk of mouth, throat, esophagus, and bladder cancer is reduced by half. After 10 years: The risk of lung cancer and bladder cancer is half that of someone who currently smokes. After 15 years: The risk of heart disease is similar to that of someone who never smoked.
Tobacco use is the leading preventable cause of cancer and cancer deaths. It causes more than lung cancer — based on current evidence, it can cause cancers of the mouth and throat, voice box, esophagus, stomach, kidney, pancreas, liver, bladder, cervix, colon and rectum, and a type of leukemia (acute myeloid leukemia).